Analysis in regards to the degenerative mind illness often known as CTE in athletes has largely centered on American soccer. However a brand new research of ice hockey gamers has discovered a hyperlink between the size of a participant’s profession and their danger of creating the situation.
Patrick Smith/Getty Pictures
cover caption
toggle caption
Patrick Smith/Getty Pictures
For years because the hyperlink between American soccer and the degenerative neurological illness known as CTE has come into focus, analysis on different sports activities had lagged behind, even for contact sports activities like ice hockey.
Now, a new study from researchers at Boston College is the most important but to determine a relationship between an athlete’s odds of creating CTE and the size of their profession in ice hockey, its authors say: the longer he performed, the extra seemingly he was to have the illness.
The research, revealed Tuesday within the journal JAMA Neurology, examined the brains of 77 deceased male ice hockey gamers, whose expertise within the sport ranged from youth hockey by skilled play. CTE can solely be identified with an post-mortem of the mind, which means it might probably solely be detected after dying.
In whole, greater than half of the hockey gamers studied had been discovered to have CTE. And the incidence of CTE rose relying on how lengthy the participant’s profession lasted: All however one of many former skilled gamers — 27 of 28 in whole, and 18 of 19 who performed within the Nationwide Hockey League — confirmed indicators of CTE, in comparison with beneath half of those that had performed on the faculty, juniors and semi-professional ranges. Of the donors whose hockey careers had been restricted to youth or highschool hockey, researchers discovered CTE in solely 10% of samples.

For years because the hyperlink between American soccer and the degenerative neurological illness often known as CTE has come into focus, analysis on different sports activities had lagged behind, even for contact sports activities like ice hockey.
Norman Y. Lono/Getty Pictures
cover caption
toggle caption
Norman Y. Lono/Getty Pictures
“We all know much less in the case of hockey,” mentioned Dr. Jesse Mez, a professor of neurology at Boston College and a co-author on the research. “Most of what we have discovered has been within the soccer area, as a result of most of our mind donors have been soccer gamers.”
As in different CTE research, researchers relied on samples that had been donated. Gamers who performed at elite ranges are overrepresented within the pattern, Mez mentioned. And choice bias is probably going, as gamers and households who organized to donate brains to researchers might have observed signs related to CTE earlier than dying, corresponding to temper swings, reminiscence points or complications.
“That means we will have extra folks with CTE within the mind financial institution than we might within the technology inhabitants,” he mentioned. “That being mentioned, while you’re discovering it in nearly the entire NHL gamers within the mind financial institution, it’s nonetheless very regarding.”
What the research doesn’t set up is how seemingly a hockey participant is to develop CTE. “With every extra yr performed, the chance will increase,” Mez mentioned. “However we do not know what absolutely the danger is for a given quantity of play within the technology inhabitants.”
Over the previous 15 years, as consciousness of the hazard of head impacts has grown, all ranges of organized hockey have taken steps to cut back the chance.
Nonetheless, in an interview last year with NPR, Nationwide Hockey League commissioner Gary Bettman denied a hyperlink between skilled hockey and CTE.
“We take heed to the medical opinions on CTE, and I do not imagine there was any documented research that means that parts of our sport end in CTE,” Bettman mentioned. “There have been remoted instances of gamers who’ve performed the sport [who] have had CTE. However it does not imply that it essentially got here from enjoying within the NHL.”
Soccer and hockey, Bettman continued, “aren’t comparable by way of the quantity of head contact.”
Analysis has proven that repeated head impacts amassed over the course of an athlete’s enjoying profession can result in CTE, regardless of the game. Apart from American soccer and ice hockey, Boston College researchers have additionally identified the illness in samples from athletes who performed soccer, rugby and wrestling.
But, at the same time as consciousness has grown, advocates say extra steps could possibly be taken to make hockey safer in any respect ranges of play. “I do not assume we’re the place we should be but,” mentioned Kerry Goulet, a former skilled hockey participant who co-founded StopConcussions, a corporation that works to mitigate head accidents in hockey and different sports activities.
Ice hockey has distinctive challenges in comparison with sports activities like soccer or soccer, Goulet mentioned. As a result of the sport is performed on a tough floor — ice — and the sphere of play is surrounded by boards and glass, some impacts are inevitable. Gamers transfer at excessive speeds and routinely collide with one another or the boards.
“I did get hit from behind. I did fall down. I did bang my head in opposition to the boards,” Goulet mentioned.
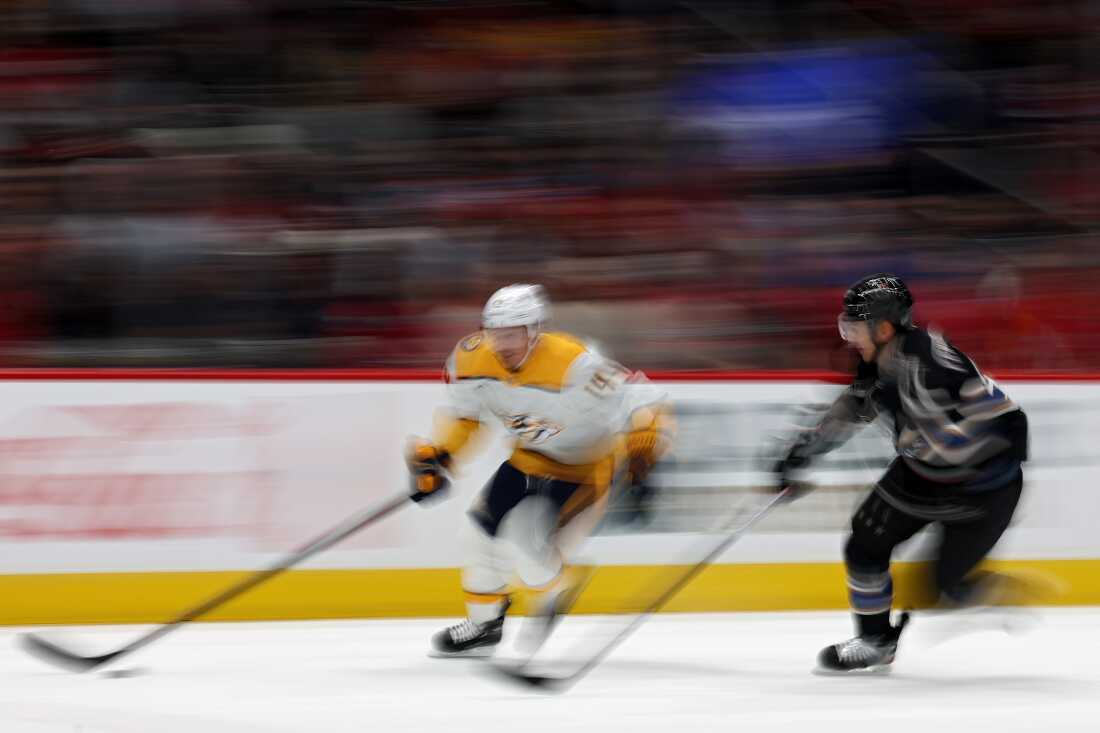

Ice hockey has distinctive components that may enhance the chance of hits to the top, consultants mentioned, together with the onerous enjoying floor, the boards and glass that encompass the ice and the pace at which elite gamers compete.
Patrick Smith/Getty Pictures
cover caption
toggle caption
Patrick Smith/Getty Pictures
He estimates that he sustained maybe 20 concussions over the course of his enjoying profession — solely three of them formally identified — and numerous different hits to his head and physique. “I bear in mind these forms of incidents the place hastily these black spots had been round me as sort of confused and dazed.” Within the years since his retirement, Goulet has skilled despair, even suicidality, he mentioned, signs that he hyperlinks to the hits to his head he skilled as a participant.
In at present’s sport, gamers at elite ranges are larger, sooner and stronger than they had been many years in the past. Gamers in any respect ranges practice year-round, slightly than within the winter alone. However rule adjustments and enforcement have made the sport extra secure, particularly for youthful gamers, who characterize nearly all of those that play the game, mentioned Dr. Michael Stuart, the chief medical officer for USA Hockey and a professor emeritus on the Mayo Clinic.
“There’s now a zero tolerance for any hit to the top. It is a penalty,” Stuart mentioned. “And a few of these extra egregious actions on the ice now carry very strict penalties, hopefully to dissuade gamers from getting in a harmful state of affairs with themselves or their opponent.”
In 2011, USA Hockey banned physique checking for boys aged 12 and beneath. The identical yr, the NHL created its first Division of Participant Security and started to penalize all hits through which a participant’s head was the principal level of contact — a transfer that decreased the incidence of concussions within the league, a study found last year.
Nonetheless, Stuart, who additionally works as guide for the NHL Gamers’ Affiliation, believes the NHL may do extra to implement guidelines in opposition to harmful play and improve penalties for harmful hits in opposition to the boards or aggressive checks from behind. “These should be closely scrutinized and aggressively penalized as a way to dissuade the sort of conduct,” he mentioned. He has additionally lengthy advocated for a ban on fights within the NHL, which have declined over time however nonetheless happen in about 20% of video games.
![[original_title]](https://rawnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/urlhttp3A2F2Fnpr-brightspot.s3.amazonaws.com2F932F562F820a76464abfb7bee06821fbe6a32Fgettyimages-2187488329-1024x576.jpg)