The James Webb Area Telescope has noticed six doubtless rogue worlds—objects with planetlike plenty however untethered from any star’s gravity—together with the lightest ever recognized with a dusty disk round it.
The elusive objects provide new proof that the identical cosmic processes that give beginning to stars might also play a standard position in making objects solely barely greater than Jupiter.
“We’re probing the very limits of the star forming course of,” mentioned lead writer Adam Langeveld, an astrophysicist at Johns Hopkins College. “If in case you have an object that appears like a younger Jupiter, is it doable that it may have change into a star underneath the precise circumstances? That is essential context for understanding each star and planet formation.”
The findings come from Webb’s deepest survey of the younger nebula NGC1333, a star-forming cluster a few thousand light-years away within the Perseus constellation. A brand new picture from the survey released today by the European Space Agency exhibits NGC1333 glowing with dramatic shows of interstellar mud and clouds. A paper detailing the survey’s findings has been accepted for publication in The Astronomical Journal.
Webb’s information counsel the found worlds are fuel giants 5–10 occasions extra large than Jupiter. Meaning they’re among the many lowest-mass objects ever discovered to have grown from a course of that will usually produce stars and brown dwarfs, objects straddling the boundary between stars and planets that by no means ignite hydrogen fusion and fade over time.
“We used Webb’s unprecedented sensitivity at infrared wavelengths to seek for the faintest members of a younger star cluster, looking for to handle a basic query in astronomy: How mild an object can kind like a star?” mentioned Johns Hopkins Provost Ray Jayawardhana, an astrophysicist and senior writer of the examine. “It seems the smallest free-floating objects that kind like stars overlap in mass with large exoplanets circling close by stars.”
The telescope’s observations revealed no objects decrease than 5 Jupiter plenty regardless of possessing enough sensitivity to detect such our bodies. That is a robust indication that any stellar objects lighter than this threshold usually tend to kind the best way planets do, the authors concluded.
“Our observations affirm that nature produces planetary mass objects in a minimum of two alternative ways—from the contraction of a cloud of fuel and mud, the best way stars kind, and in disks of fuel and mud round younger stars, as Jupiter in our personal photo voltaic system did,” Jayawardhana mentioned.
Probably the most intriguing of the starless objects can also be the lightest, having an estimated mass of 5 Jupiters (about 1,600 Earths). The presence of a dusty disk means the article nearly definitely fashioned like a star, as house mud usually spins round a central object within the early phases of star formation, mentioned Langeveld, a postdoctoral researcher in Jayawardhana’s group.
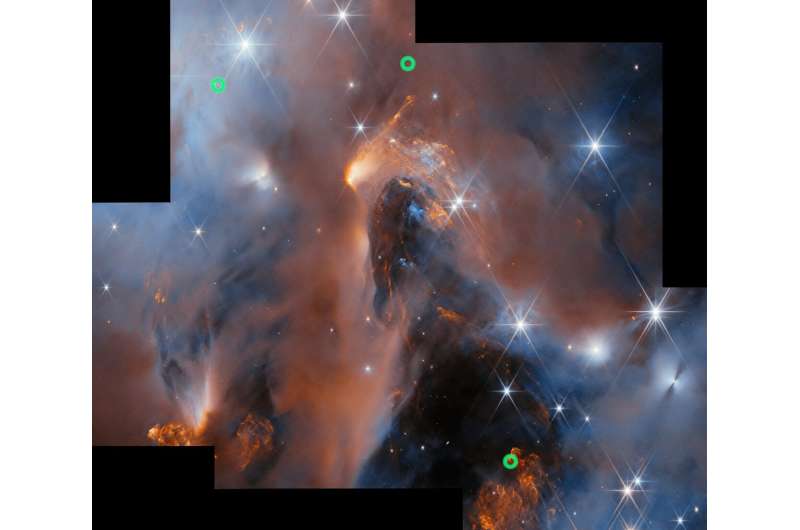

Disks are additionally a prerequisite for the formation of planets, suggesting the observations might also have essential implications for potential “mini” planets.
“These tiny objects with plenty comparable to massive planets could themselves have the ability to kind their very own planets,” mentioned co-author Aleks Scholz, an astrophysicist on the College of St Andrews. “This could be a nursery of a miniature planetary system, on a scale a lot smaller than our photo voltaic system.”
Utilizing the NIRISS instrument on Webb, the astronomers measured the infrared mild profile (or spectrum) of each object within the noticed portion of the star cluster and reanalyzed 19 recognized brown dwarfs. Additionally they found a brand new brown dwarf with a planetary-mass companion, a uncommon discovering that challenges theories of how binary techniques kind.
“It is doubtless that such a pair fashioned the best way binary star techniques do, from a cloud fragmenting because it contracted,” Jayawardhana mentioned. “The variety of techniques that nature has produced is exceptional and pushes us to refine our fashions of star and planet formation.”
Rogue worlds could originate from collapsing molecular clouds that lack the mass for the nuclear fusion that powers stars. They’ll additionally kind when fuel and mud in disks round stars coalesce into planetlike orbs which are ultimately ejected from their star techniques, most likely due to gravitational interactions with different our bodies.
These free-floating objects blur the classifications of celestial our bodies as a result of their plenty overlap with fuel giants and brown dwarfs. Regardless that such objects are thought-about uncommon within the Milky Method galaxy, the brand new Webb information present they account for about 10% of celestial our bodies within the focused star cluster.
Within the coming months, the crew will examine extra of the faint objects’ atmospheres and examine them to heavier brown dwarfs and fuel large planets. They’ve additionally been awarded time on the Webb telescope to check comparable objects with dusty disks to discover the opportunity of forming mini planetary techniques resembling Jupiter’s and Saturn’s quite a few moons.
Different authors are Koraljka Mužić and Daniel Capela of Universidade de Lisboa; Loïc Albert, René Doyon, and David Lafrèniere of Université de Montréal; Laura Flagg of Johns Hopkins; Matthew de Furio of College of Texas at Austin; Doug Johnstone of Herzberg Astronomy and Astrophysics Analysis Centre; and Michael Meyer of College of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Extra info:
The JWST/NIRISS Deep Spectroscopic Survey for Younger Brown Dwarfs and Free-Floating Planets, The Astronomical Journal (2024). DOI: 10.3847/1538-3881/ad6f0c
Supplied by
Johns Hopkins University
Quotation:
In six new rogue worlds, Webb Telescope finds extra star beginning clues (2024, August 27)
retrieved 27 August 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-08-rogue-worlds-webb-telescope-star.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.
![[original_title]](https://rawnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/in-six-new-rogue-world-1024x838.jpg)