A nurse takes care of a affected person at a hospital close to Lima, Peru. The nation skilled an outbreak of dengue fever in 2024 — a sample that was replicated in lots of international locations around the globe. A brand new research suggests local weather change could also be contributing to the unfold of the mosquito-borne illness.
Juan Carlos Cisneros/AFP by way of Getty Photographs
conceal caption
toggle caption
Juan Carlos Cisneros/AFP by way of Getty Photographs
In 2023, some 6 million instances of dengue fever have been reported worldwide — greater than ever earlier than. Then, 2024 blew that report away. Greater than 12 million instances have been reported worldwide up to now this yr.
Case numbers had been rising for years earlier than that, although. Now, a brand new research awaiting peer assessment means that local weather change has doubtless played a significant role in the expansion of the disease from 1995 to 2014, in response to an evaluation offered in November on the American Society of Tropical Drugs and Hygiene convention in New Orleans. Over that point interval, local weather change elevated the caseload by roughly 20% throughout the 21 international locations within the research — all locations the place dengue fever was already established, like Indonesia, India and Brazil.
The numbers might skyrocket with additional local weather change, even past the record-breaking case numbers from the previous few years, says Erin Mordecai, an infectious illness skilled at Stanford College and one of many authors of the brand new evaluation.
“Lots of the locations within the research area are going to greater than double their projected dengue incidence” if human-caused local weather change continues to aggressively warmth up the planet, she says. However the development might be contained — not stopped, however at the least minimized — if local weather motion retains international temperatures in test, she stresses.
Dengue fever is the most typical tropical illness on the planet. In a few quarter of instances, it could possibly drive painful fever and the feeling of aching joints and bones results in its widespread identify “breakbone fever.” In a small percentage of cases — and most frequently when somebody contracts the illness for a second time — it may be deadly.
Thousands and thousands of instances of dengue fever play out yearly worldwide. However there may be presently no generally accessible vaccine for adults, and little past palliative care to handle the illness as soon as contracted.
Local weather fingerprints on dengue fever
Dengue fever is unfold between individuals by two species of mosquitoes, Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti.
“Mosquitoes are exothermic,” or cold-blooded, Mordecai explains. “So when the temperature will get hotter, all the pieces that their physique does hastens.”
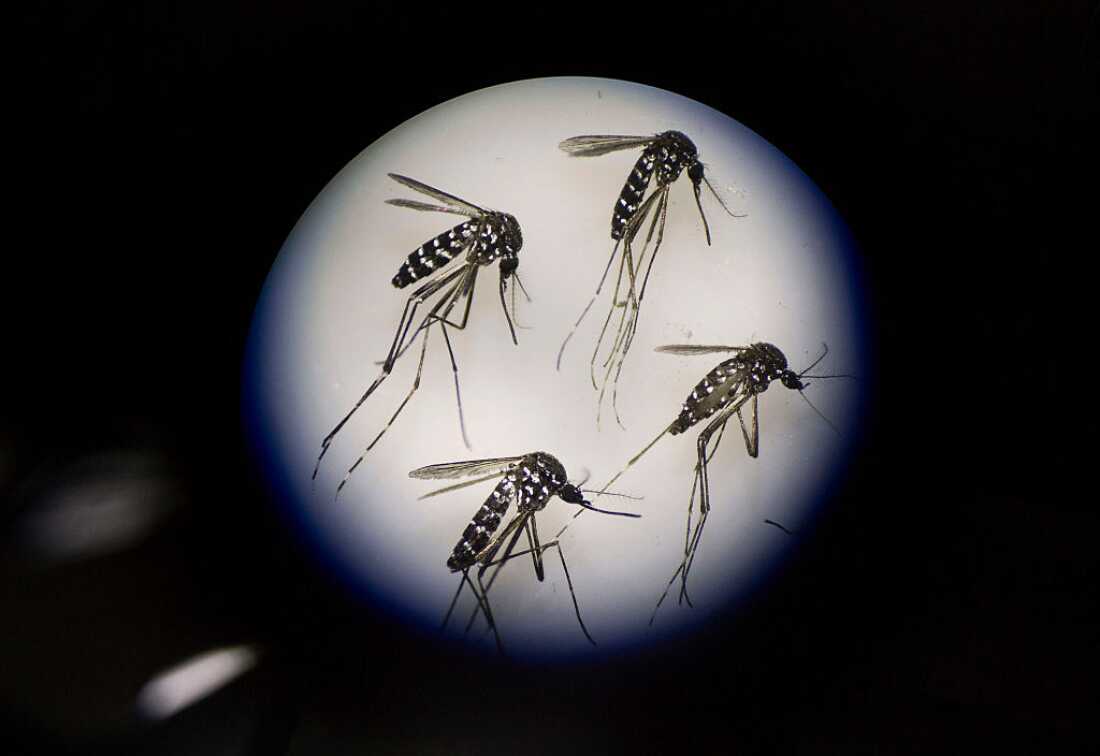
Dengue fever is unfold by two species of mosquito. Grownup females of a kind of species, Aedes albopictus, are examined underneath a microscope. Every species thrives underneath explicit climate circumstances. Local weather change is increasing these very best zones into many new elements of the world, growing the variety of instances.
Kevin Frayer/Getty Photographs
conceal caption
toggle caption
Kevin Frayer/Getty Photographs
Mosquitoes develop sooner. They extra successfully replicate the virus of their guts. They even chunk extra aggressively as temperatures heat towards these very best ranges.
Earlier analysis in laboratories confirmed that these species of mosquitoes thrived inside a predictable temperature vary. For Aedes albopictus, the best Goldilocks temperature was roughly 79 levels Fahrenheit. For Aedes aegypti, it was barely greater, a balmy 84 levels.
There’s a built-in restrict, says Mordecai: Too far previous these Goldilocks temperatures and mosquitoes undergo and begin to die. And a useless mosquito cannot unfold illness.
The researchers might observe modifications in temperature over time in tandem with modifications in reported illness instances. And utilizing local weather fashions, they might tease out how a lot of the temperature rise in every location might be blamed on human-caused local weather change — a method referred to as attribution. Then, utilizing subtle statistical methods borrowed from economics, they might hyperlink the human-driven temperature will increase with elevated caseloads.
Related methods are actually generally used to diagnose human-caused local weather change’s fingerprint on excessive climate like warmth waves or hurricanes. However the brand new evaluation is among the first to explicitly hyperlink local weather change to modifications in infectious illness instances.
“Understanding how a lot of the rise in illness could be attributed to local weather may give us extra confidence in our predictions for a way infections are going to answer future local weather modifications,” says Marta Shocket, a illness ecologist at Lancaster College within the U.Ok. “And this might help us do higher long-term planning for a way we allocate totally different public well being assets.”
Total, the researchers discovered that temperature circumstances typically favor the growth of the illness, particularly in areas like highland Mexico, Bolivia and Brazil. Hotter areas, like Thailand and Cambodia, have seen development as effectively, however smaller marginal will increase as a result of temperatures have been already close to the mosquitoes’ higher limits.
They might additionally look into the long run to see the place dangers would possibly emerge — and what number of instances might be in retailer in a fair hotter future. Many elements of South America, notably these which can be on the cooler finish of the mosquitoes’ most popular temperature vary now, might see their caseloads double by the center of the century if warming continues on its present trajectory. Solely Cambodia was projected to see a drop in instances.
“Lots of areas which can be extra temperate will change into extra appropriate — and what’s scary is that it occurs to overlap so much with actually densely populated cities,” says Jamie Caldwell, an infectious illness researcher at Princeton College who was not concerned within the research.
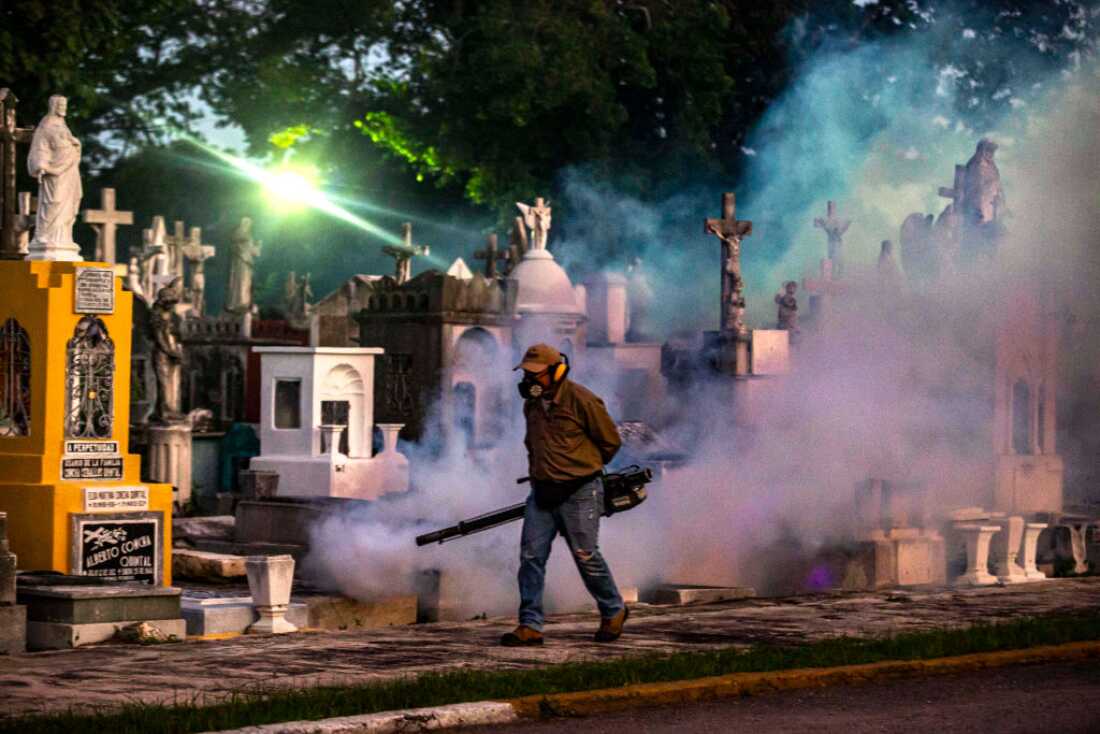
A well being employee dispenses insecticide with fogging machines to kill mosquitoes spreading dengue fever forward of the Day of the Useless celebrations in Merida, Mexico. 2024 broke data for the variety of dengue fever instances reported worldwide.
Hugo Borges/AFP by way of Getty Photographs
conceal caption
toggle caption
Hugo Borges/AFP by way of Getty Photographs
The research didn’t embrace international locations the place dengue fever remains to be uncommon, a class which incorporates the U.S. However the variety of instances inside U.S. borders has additionally risen sharply in recent times, in sizzling, humid areas like Florida and southern Texas. However in 2023, a number of instances of domestically acquired dengue fever have been reported for the first time in Southern California. Extra have been recognized this yr in Los Angeles County.
When dengue caseloads are excessive in the remainder of the world, it will increase the probabilities the illness could make its method into new areas, just like the U.S., says Katharine Walter, an epidemiologist on the College of Utah.
“The world is extra linked than ever earlier than, and nation borders are synthetic,” she says. “Unchecked viral transmission does not keep in a single place.”
Public well being efforts nonetheless matter — so much
A warmer planet contributes to the growth of the illness — however it’s removed from the one cause, says Benny Rice, a illness ecologist at Princeton College. Dengue fever, like different ailments unfold by “vectors” like mosquitoes or ticks, is managed by an unlimited array of things.
Urbanization — notably in unplanned developments like these bobbing up on the outskirts of cities worldwide — typically creates mosquito havens, resulting in a better probability of illness outbreaks. International journey additionally permits the illness to unfold shortly and simply between areas. Different climate components, just like the frequency and depth of rainfall or excessive climate, additionally affect the dynamics of dengue outbreaks.
In some methods, all that complexity represents alternative, says Rice. He factors out that even when local weather change influences 20% of dengue instances — or much more — that leaves 80% of instances that might be reined in. “The general public well being interventions which have existed for years are extra necessary than ever,” he says — from efforts like aggressive efforts to curb mosquito populations to creating robust native networks of medical care.
Nonetheless, the research reveals that “the local weather actually offers context for the place and when outbreaks might happen,” Cambell says.
The evaluation suggests dengue instances will proceed to skyrocket as Earth’s local weather continues to heat. By the center of the century, the variety of instances might rise by 60% as extra elements of the world enter the mosquito-friendly temperature zone.
However Mordecai says that factors to a transparent resolution: alongside the opposite public well being measures, any success at slowing Earth’s warming by lowering planet-warming emissions will reduce the dangers.
![[original_title]](https://rawnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/urlhttp3A2F2Fnpr-brightspot.s3.amazonaws.com2F4f2F562F546ed2104c95a53c3589dd4b18082Fgettyimages-2147900423-1024x576.jpg)