In July 1968, a lot work nonetheless remained to satisfy the goal President John F. Kennedy set in Might 1961, to land a person on the Moon and return him safely to the Earth earlier than the tip of the last decade. No American astronaut had flown in area because the November 1966 flight of Gemini XII, the delay largely a results of the tragic Apollo 1 fireplace. Though the Apollo spacecraft had efficiently accomplished a number of uncrewed take a look at flights, the primary crewed mission nonetheless lay three months sooner or later. The delays in getting the Lunar Module (LM) prepared for its first flight induced schedule issues, but in addition introduced a possibility for a daring step to ship the second crewed Apollo mission, the primary crewed flight of the Saturn V, on a visit to orbit the Moon. Utilizing an incremental method, three flights later NASA achieved President Kennedy’s purpose.

 Left: The charred stays of the Apollo 1 spacecraft following the tragic fireplace that claimed the lives of astronauts Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White, and Roger B. Chaffee. Center left: The primary launch of the Saturn V rocket on the Apollo 4 mission. Center proper: The primary Lunar Module in preparation for the Apollo 5 mission. Proper: Splashdown of Apollo 6, the ultimate uncrewed Apollo mission.
Left: The charred stays of the Apollo 1 spacecraft following the tragic fireplace that claimed the lives of astronauts Virgil I. “Gus” Grissom, Edward H. White, and Roger B. Chaffee. Center left: The primary launch of the Saturn V rocket on the Apollo 4 mission. Center proper: The primary Lunar Module in preparation for the Apollo 5 mission. Proper: Splashdown of Apollo 6, the ultimate uncrewed Apollo mission.
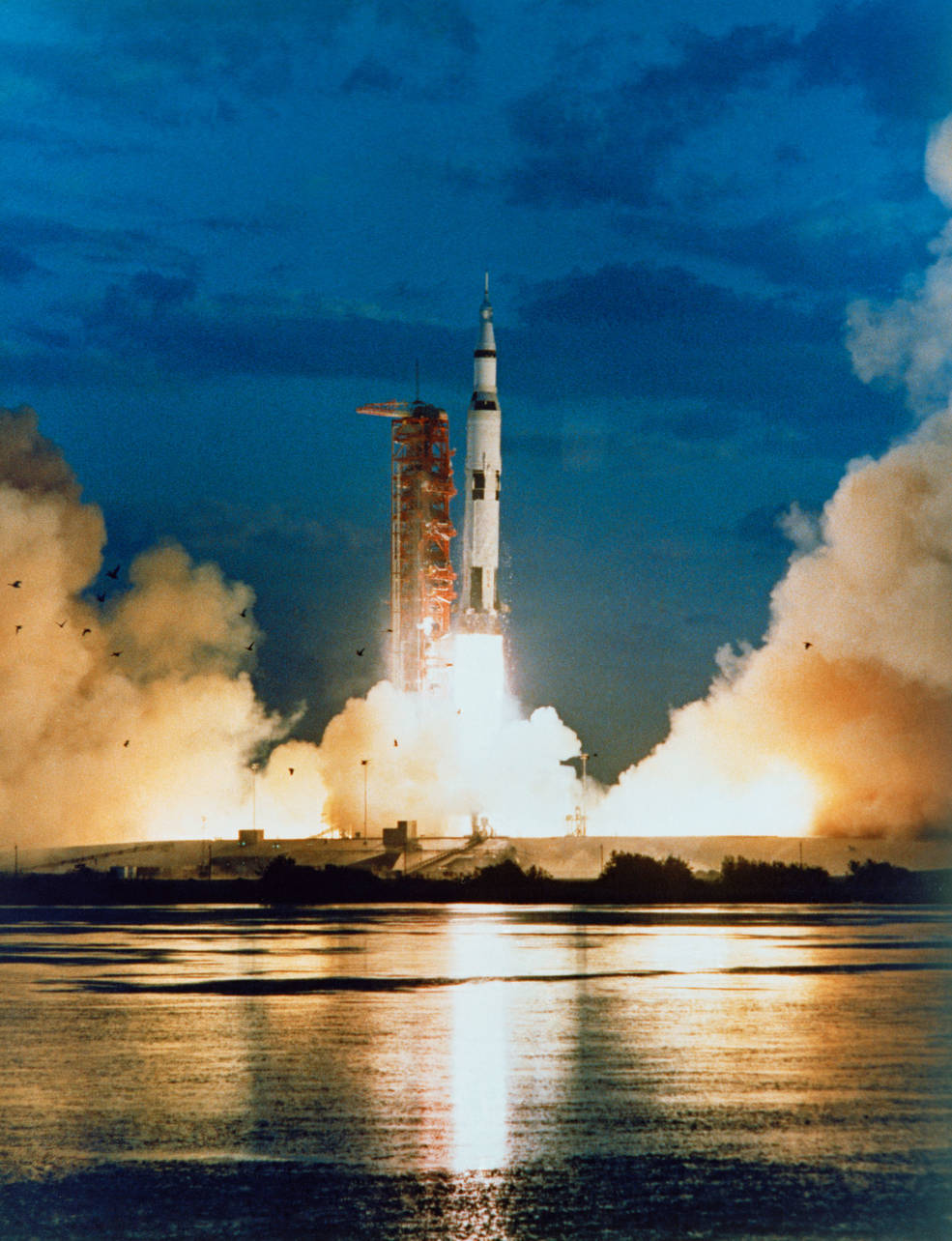
The American human spaceflight program suffered a jarring setback on Jan. 27, 1967, with the deaths of astronauts Virgil I. Grissom, Edward H. White, and Roger B. Chaffee within the Apollo 1 fire. The hearth and subsequent Investigation led to wholesale adjustments to the spacecraft, akin to the usage of fireproof supplies and redesign of the hatch to make it simple to open. The early Block I spacecraft, akin to Apollo 1, would now solely be used for uncrewed missions, with crews flying solely aboard the extra superior Block II spacecraft. The hearth and its aftermath additionally led to administration adjustments. For instance, George M. Low changed Joseph F. Shea as Apollo Spacecraft Program Supervisor. The primary Apollo mission after the fireplace, the uncrewed Apollo 4 in November 1967, included the primary launch of the Saturn V Moon rocket in addition to a 9-hour flight of a Block I Command and Service Module (CSM). Apollo 5 in January 1968 performed the primary uncrewed take a look at of the LM, and regardless of a couple of anomalies, managers thought of it profitable sufficient that they canceled a second uncrewed flight. The April 1968 flight of Apollo 6, deliberate as a near-repeat of Apollo 4, encountered a number of vital anomalies akin to first stage POGO, or extreme vibrations, and the failure of the third stage to restart, resulting in an alternate mission situation. Engineers devised an answer to the POGO drawback and managers determined that the third flight of the Saturn V would carry a crew.
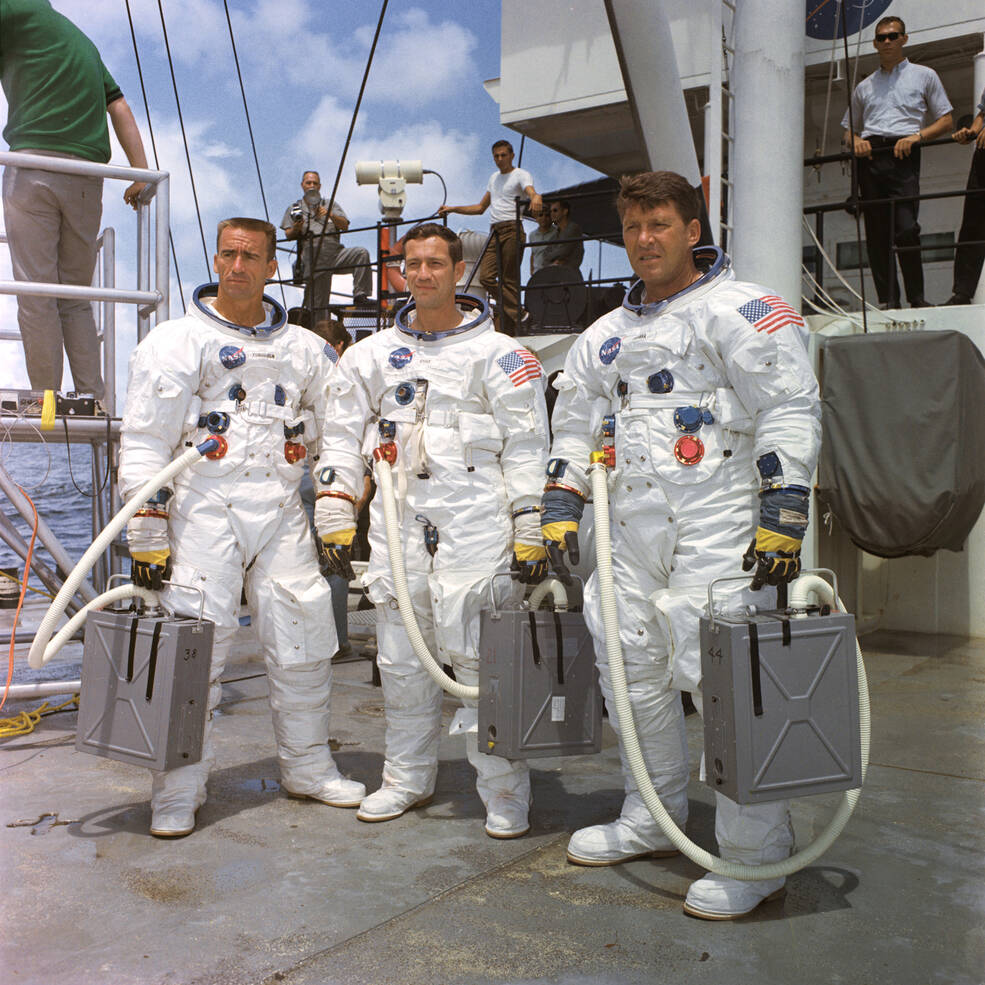

 Left: Apollo 7 astronauts R. Walter Cunningham, left, Donn F. Eisele, and Walter M. Schirra take part in water egress coaching. Center: Staff stack the Apollo 7 spacecraft on its Saturn IB rocket at Launch Pad 34. Proper: Schirra, left, Cunningham, and Eisele stand exterior the spacecraft simulator.
Left: Apollo 7 astronauts R. Walter Cunningham, left, Donn F. Eisele, and Walter M. Schirra take part in water egress coaching. Center: Staff stack the Apollo 7 spacecraft on its Saturn IB rocket at Launch Pad 34. Proper: Schirra, left, Cunningham, and Eisele stand exterior the spacecraft simulator.
As of July 1968, NASA’s plan referred to as for 2 crewed Apollo flights in 1968 and as much as 5 in 1969 to realize the primary lunar touchdown to satisfy President Kennedy’s deadline, with every mission incrementally constructing on the success of the earlier ones. The primary mission, Apollo 7, would return American astronauts to area following a 23-month hiatus. Deliberate for October 1968, the crew of Walter M. Schirra, Donn F. Eisele, and R. Walter Cunningham would launch atop a Saturn IB rocket and conduct a shakedown flight of the Block II CSM in Earth orbit, together with testing the Service Propulsion System engine, important on later lunar missions for entering into and out of lunar orbit. The flight plan remained open-ended, however managers anticipated to finish a full-duration 11-day mission, ending with a splashdown within the Atlantic Ocean. Preparations for Apollo 7 proceeded effectively throughout the summer season of 1968. Staff had stacked the two-stage Saturn IB rocket on Launch Pad 34 again in April. In KSC’s Manned Spacecraft Operations Constructing (MSOB), Schirra, Eisele, and Cunningham accomplished altitude chamber exams of their spacecraft, CSM-101, on July 26 adopted by their backups three days later. Staff trucked the spacecraft to the launch pad on Aug. 9 for mating with the rocket. Amongst main milestones, Schirra, Eisele, and Cunningham accomplished water egress coaching within the Gulf of Mexico on Aug. 5, along with spending time within the spacecraft simulators at KSC and on the Manned Spacecraft Heart (MSC), now NASA’s Johnson House Heart in Houston.
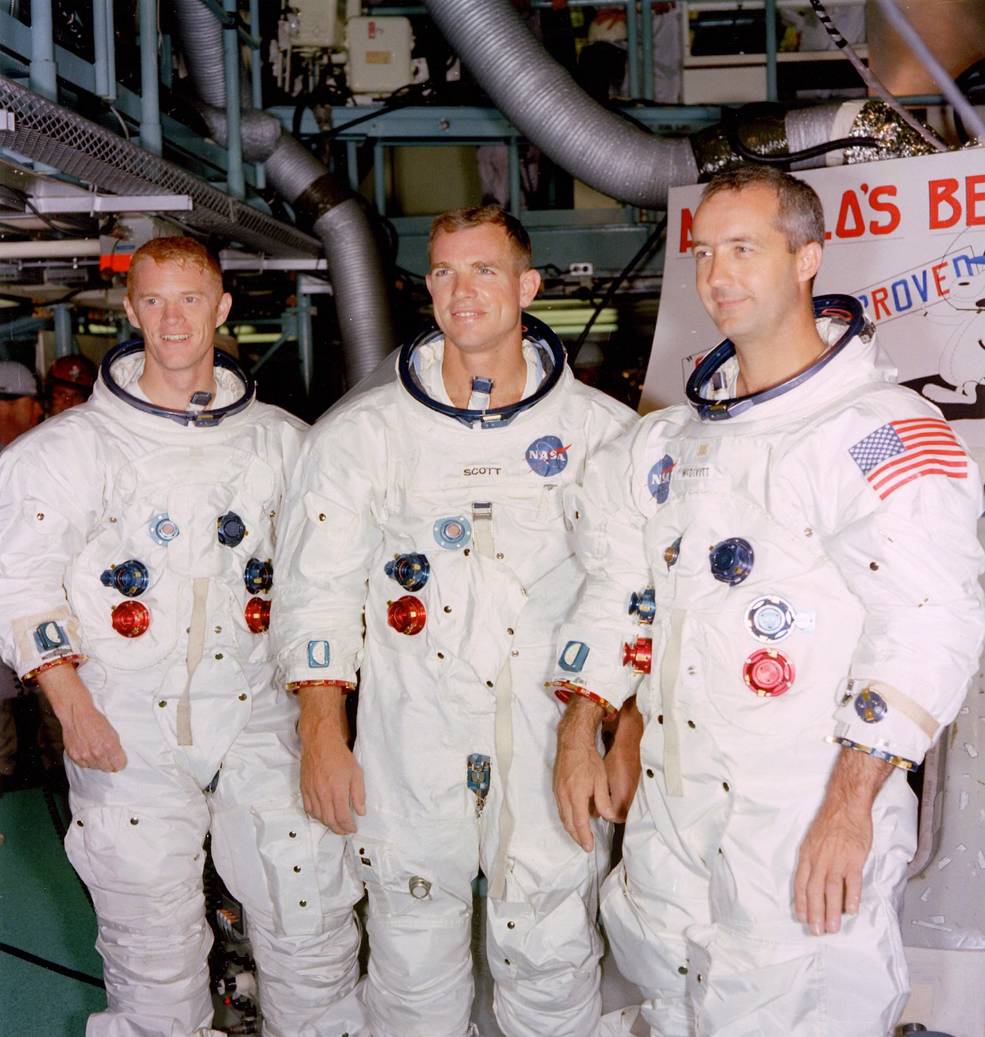
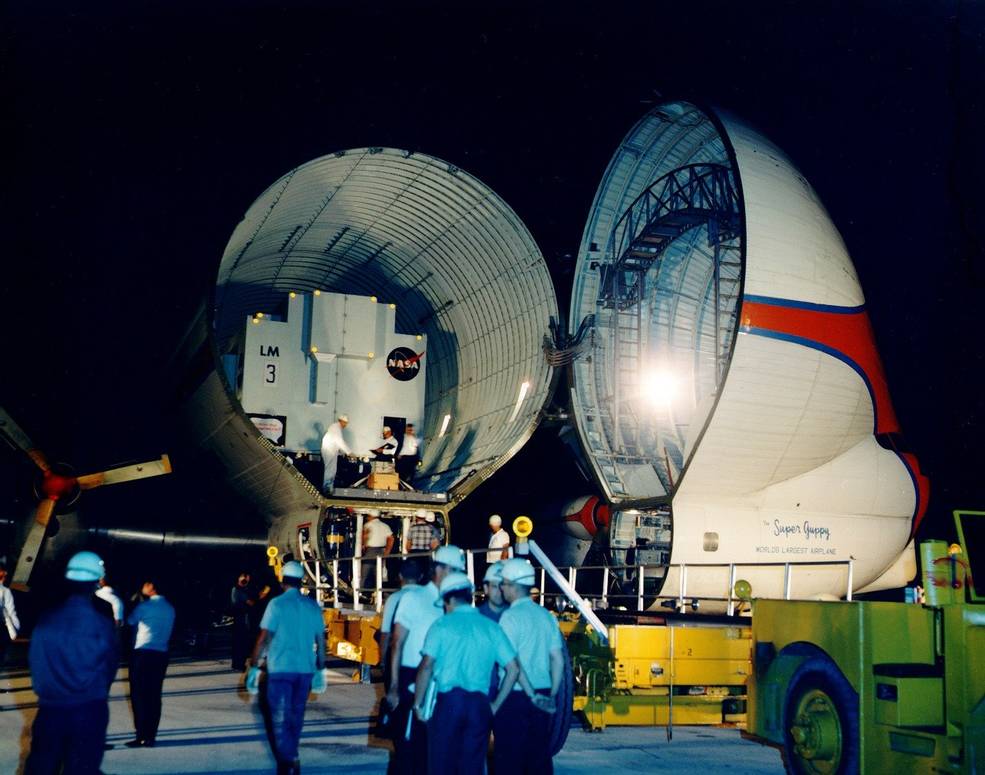


 Left: The unique Apollo 8 crew of Russell L. Schweickart, left, David R. Scott, and James A. McDivitt throughout coaching in June 1968. Center: Lunar Module-3 arrives at NASA’s Kennedy House Heart (KSC) in Florida in June 1968. Proper: In July 1968, staff in KSC’s Automobile Meeting Constructing stack the Saturn V rocket for the Apollo 8 mission.
Left: The unique Apollo 8 crew of Russell L. Schweickart, left, David R. Scott, and James A. McDivitt throughout coaching in June 1968. Center: Lunar Module-3 arrives at NASA’s Kennedy House Heart (KSC) in Florida in June 1968. Proper: In July 1968, staff in KSC’s Automobile Meeting Constructing stack the Saturn V rocket for the Apollo 8 mission.
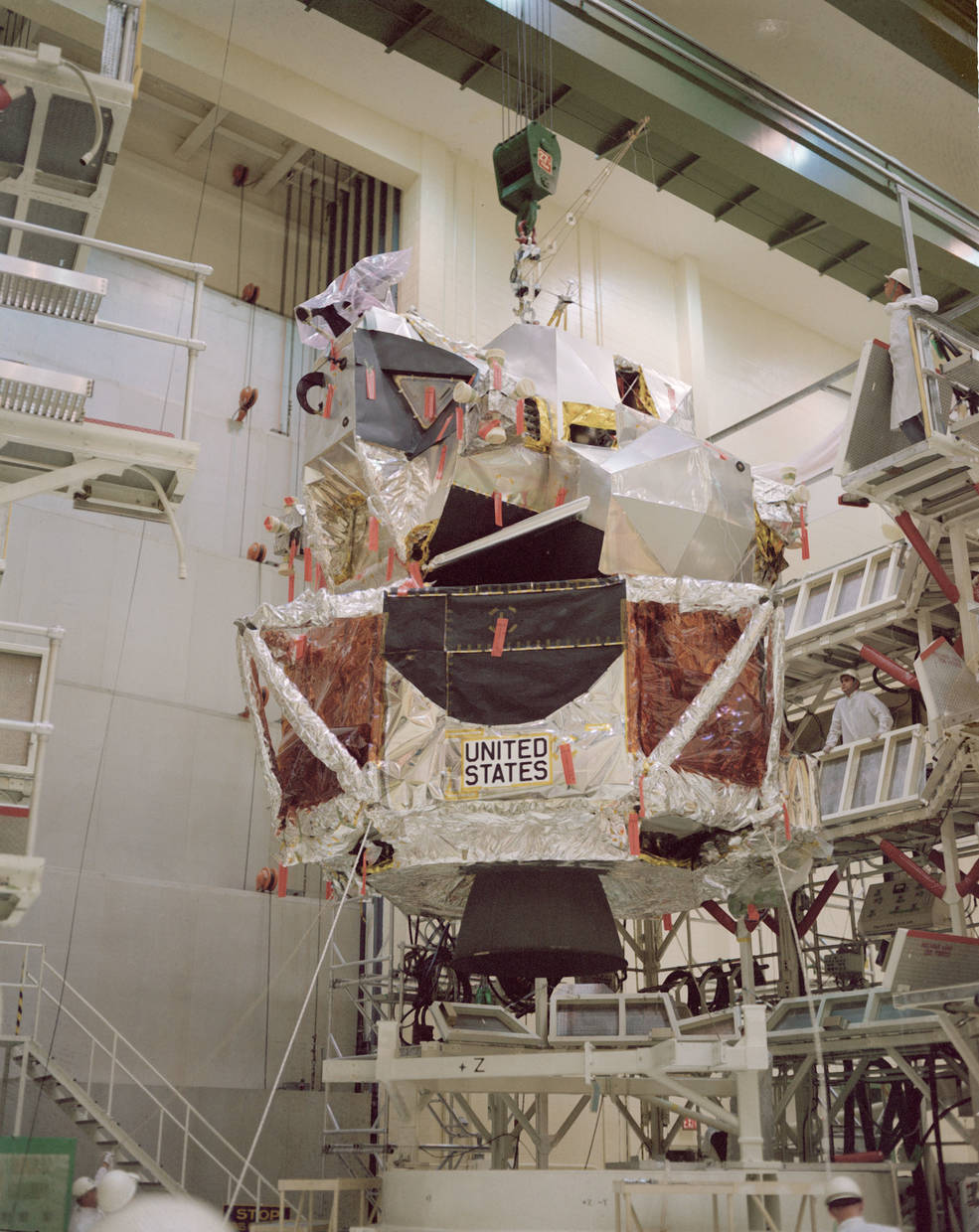
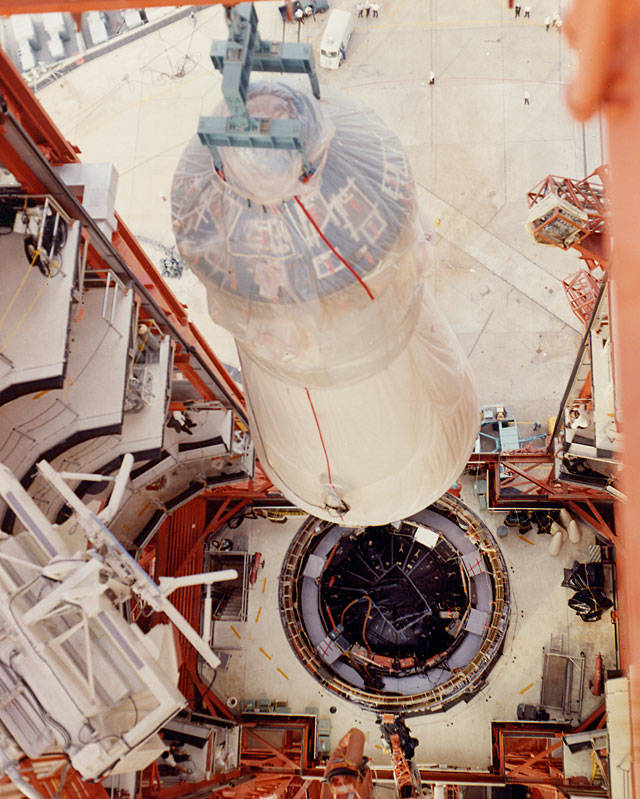
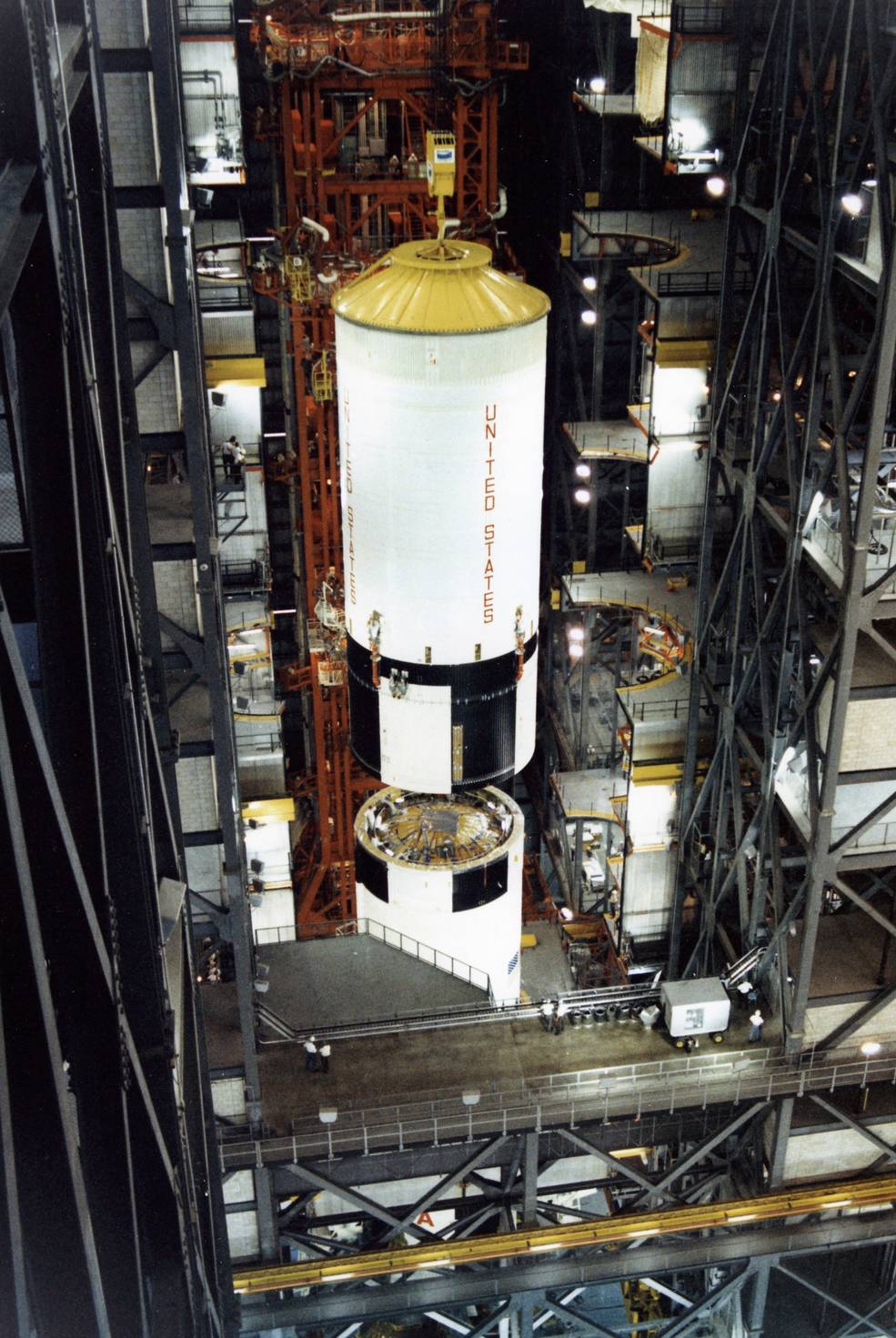
The second flight, concentrating on a December 1968 launch, would function the primary crewed launch of the Saturn V rocket. The Apollo 8 crew of James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart would conduct the primary crewed take a look at of the LM within the relative security of low Earth orbit. McDivitt and Schweickart would fly the LM on its impartial mission, together with separating the ascent stage from the descent stage to simulate a takeoff from the Moon, whereas Scott remained within the CSM. After redocking, Schweickart would conduct a spacewalk to apply an exterior switch between the 2 autos. Staff accomplished stacking the three-stage Saturn V rocket (SA-503) in KSC’s Automobile Meeting Constructing (VAB) on Aug. 14. The primary part of the spacecraft, LM-3, arrived at KSC on June 9, whereas CSM-103, arrived on Aug. 12. Staff within the MSOB started to arrange each spacecraft for flight.
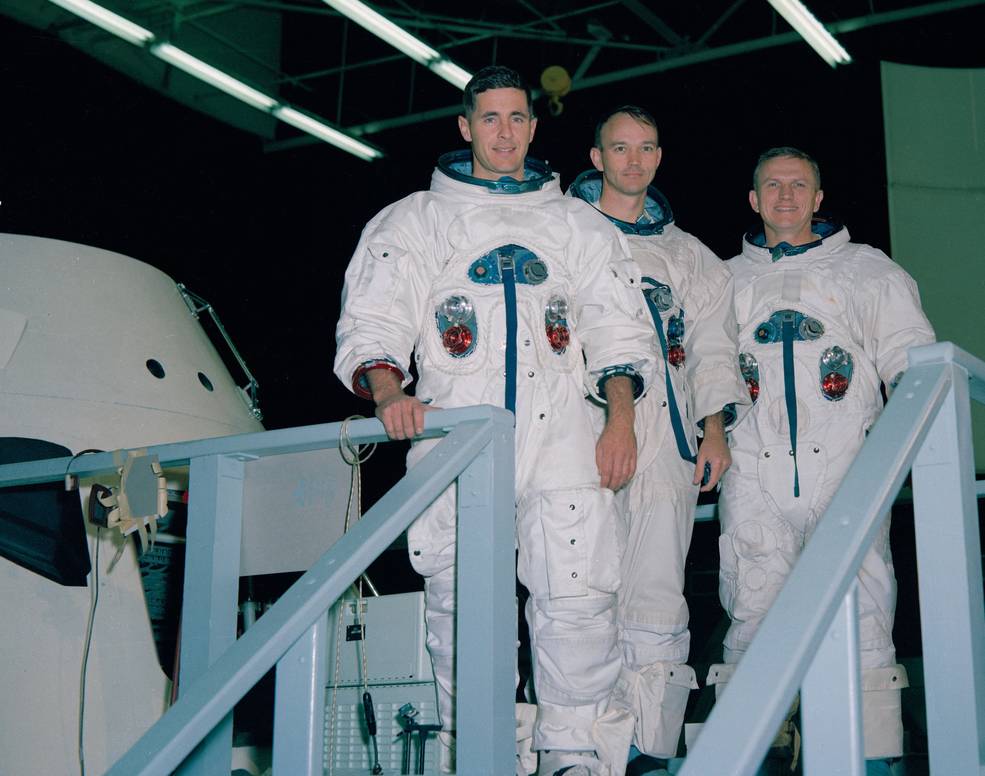

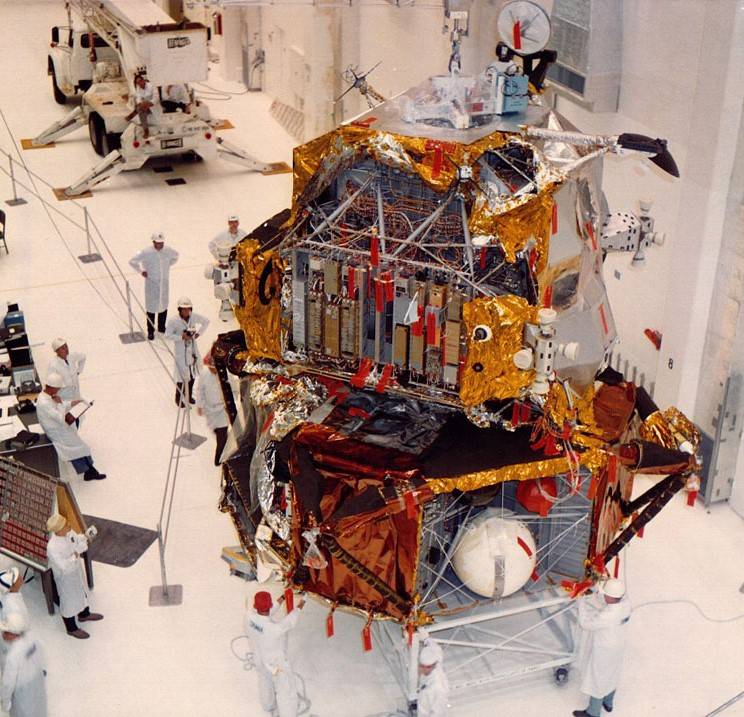
 Left: The unique Apollo 9 crew of William A. Anders, left, Michael Collins, and Frank Borman throughout coaching in March 1968. Center: Lunar Module-3 throughout preflight processing at NASA’s Kennedy House Heart (KSC) in Florida in August 1968. Proper: Following the revision of the mission plans for Apollo 8 and 9 and crew adjustments, the Apollo 8 crew of James A. Lovell, Anders, and Borman stand earlier than their Saturn V rocket because it rolls out of KSC’s Automobile Meeting Constructing in October 1968.
Left: The unique Apollo 9 crew of William A. Anders, left, Michael Collins, and Frank Borman throughout coaching in March 1968. Center: Lunar Module-3 throughout preflight processing at NASA’s Kennedy House Heart (KSC) in Florida in August 1968. Proper: Following the revision of the mission plans for Apollo 8 and 9 and crew adjustments, the Apollo 8 crew of James A. Lovell, Anders, and Borman stand earlier than their Saturn V rocket because it rolls out of KSC’s Automobile Meeting Constructing in October 1968.
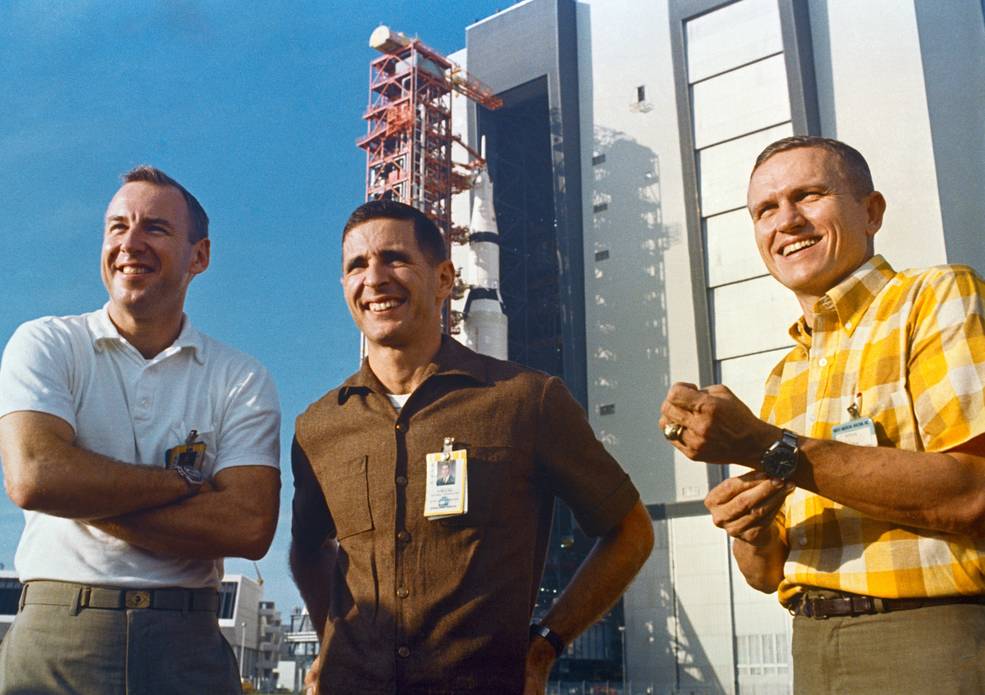
The third flight, deliberate for early 1969, and flown by Frank Borman, Michael Collins, and William A. Anders, would basically repeat the Apollo 8 mission, however on the finish would fireplace the SPS engine to lift the excessive level of their orbit to 4,600 miles after which simulate a reentry at lunar return velocity to check the spacecraft’s warmth defend. On July 23, Collins underwent surgery for a bone spur in his neck, and on August 8, NASA introduced that James A. Lovell from the backup crew would take his place. Later missions in 1969 would progress to sending the CSM and LM mixture to lunar orbit, resulting in the primary touchdown earlier than the tip of the 12 months. Development of the rocket and spacecraft parts for these future missions continued at numerous contractor amenities across the nation.
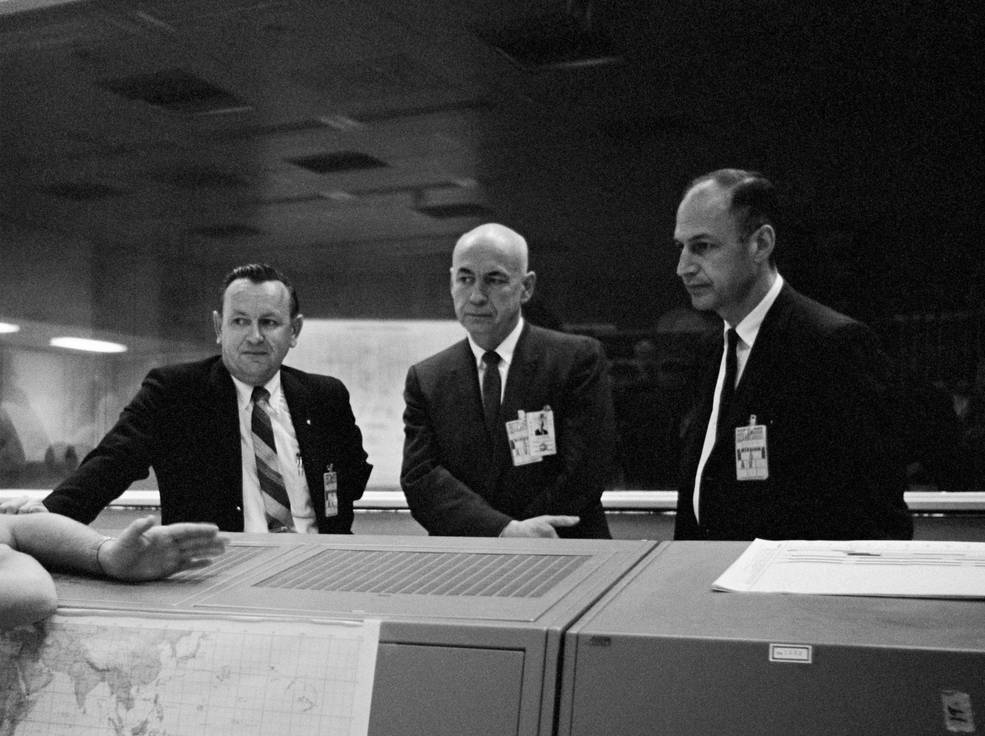


 Left: In Mission Management throughout the Apollo 6 mission, Director of Flight Crew Operations Christopher C. Kraft, left, Director of the Manned Spacecraft Heart, now NASA’s Johnson House Heart in Houston Robert R. Gilruth, and Apollo Spacecraft Program Supervisor George M. Low. Center left: Chief of Flight Crew Operations Donald Okay. “Deke” Slayton. Center proper: Director of NASA’s Kennedy House Heart in Florida Kurt H. Debus. Proper: Director of NASA’s Marshall House Flight Heart in Huntsville, Alabama.
Left: In Mission Management throughout the Apollo 6 mission, Director of Flight Crew Operations Christopher C. Kraft, left, Director of the Manned Spacecraft Heart, now NASA’s Johnson House Heart in Houston Robert R. Gilruth, and Apollo Spacecraft Program Supervisor George M. Low. Center left: Chief of Flight Crew Operations Donald Okay. “Deke” Slayton. Center proper: Director of NASA’s Kennedy House Heart in Florida Kurt H. Debus. Proper: Director of NASA’s Marshall House Flight Heart in Huntsville, Alabama.
Challenges to this plan started to come up in June 1968. Managers’ greatest concern centered across the readiness of LM-3. After its supply to KSC on June 9, managers realized the car wanted rather more work than anticipated and it could not meet the deliberate December Apollo 8 launch date. Greatest estimates put its flight readiness no sooner than February 1969. That sort of delay would jeopardize assembly President Kennedy’s fast-approaching deadline. To complicate issues, intelligence studies indicated that the Soviets have been near sending cosmonauts on a trip around the Moon, probably earlier than the tip of the 12 months, and in addition getting ready to check a Saturn V-class rocket for a Moon touchdown mission.
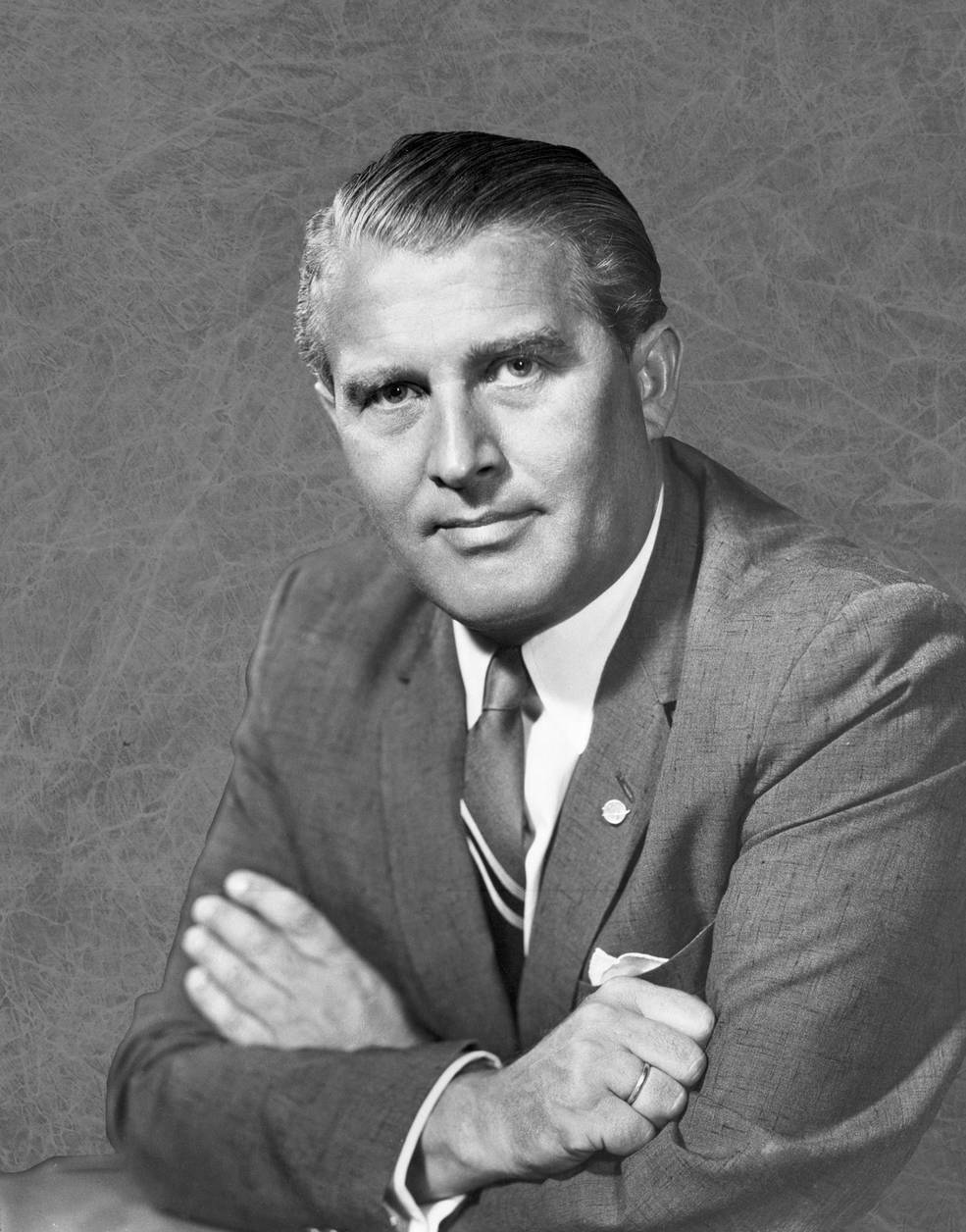
Apollo Spacecraft Program Supervisor Low formulated a plan each audacious and dangerous. With no LM, an Earth orbital Apollo 8 mission would merely repeat Apollo 7’s and never advance this system very a lot. By sending the CSM on a mission across the Moon, and even to orbit the Moon, NASA would achieve helpful expertise in navigation and communications at lunar distances. To hunt administration help for his plan, on Aug. 9 Low met with MSC Director Robert R. Gilruth, who supported the proposal. They referred to as in Christopher C. Kraft, director of flight operations, for his opinion. Two days earlier, Low had requested Kraft to evaluate the feasibility of a lunar orbit mission for Apollo 8, and Kraft deemed it achievable from a floor management and spacecraft laptop standpoint. Chief of Flight Crew Operations Donald K. “Deke” Slayton joined the dialogue, and all agreed to hunt help for the plan from the administrators of KSC and of NASA’s Marshall House Flight Heart (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama, in addition to NASA Headquarters (HQ) in Washington, D.C. That afternoon, the 4 flew to Huntsville and met with MSFC Director Wernher von Braun, KSC Director Kurt H. Debus, and HQ Apollo Program Director Samuel C. Phillips. By the tip of the assembly, the group recognized no insurmountable technical obstacles to the lunar mission plan, with the qualification that the Apollo 7 mission in October concluded efficiently. Von Braun had confidence that the Saturn V would carry out safely, and Debus believed KSC may help a December launch.
Slayton referred to as Borman, who was with Lovell and Anders conducting exams with their spacecraft in Downey, California. He ordered Borman to right away fly to Houston, the place he provided him command of the brand new circumlunar Apollo 8 mission, which Borman accepted. His crew would swap missions with McDivitt’s, who agreed to fly an Earth orbital take a look at of the LM in February 1969, placing that crew’s larger expertise with the LM to good use. The coaching problem fell on Borman’s crew, who now had simply 4 months to coach for a flight across the Moon.
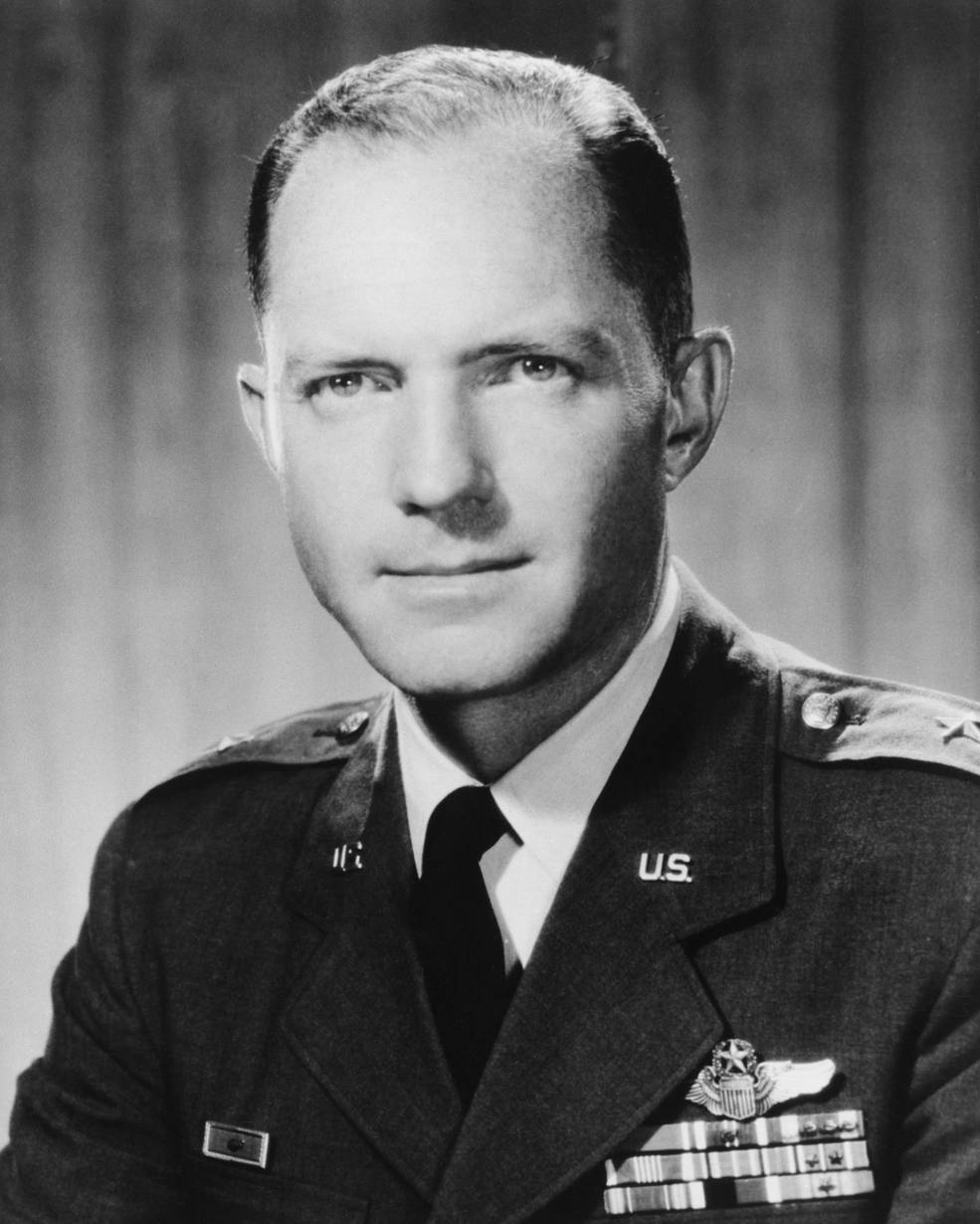
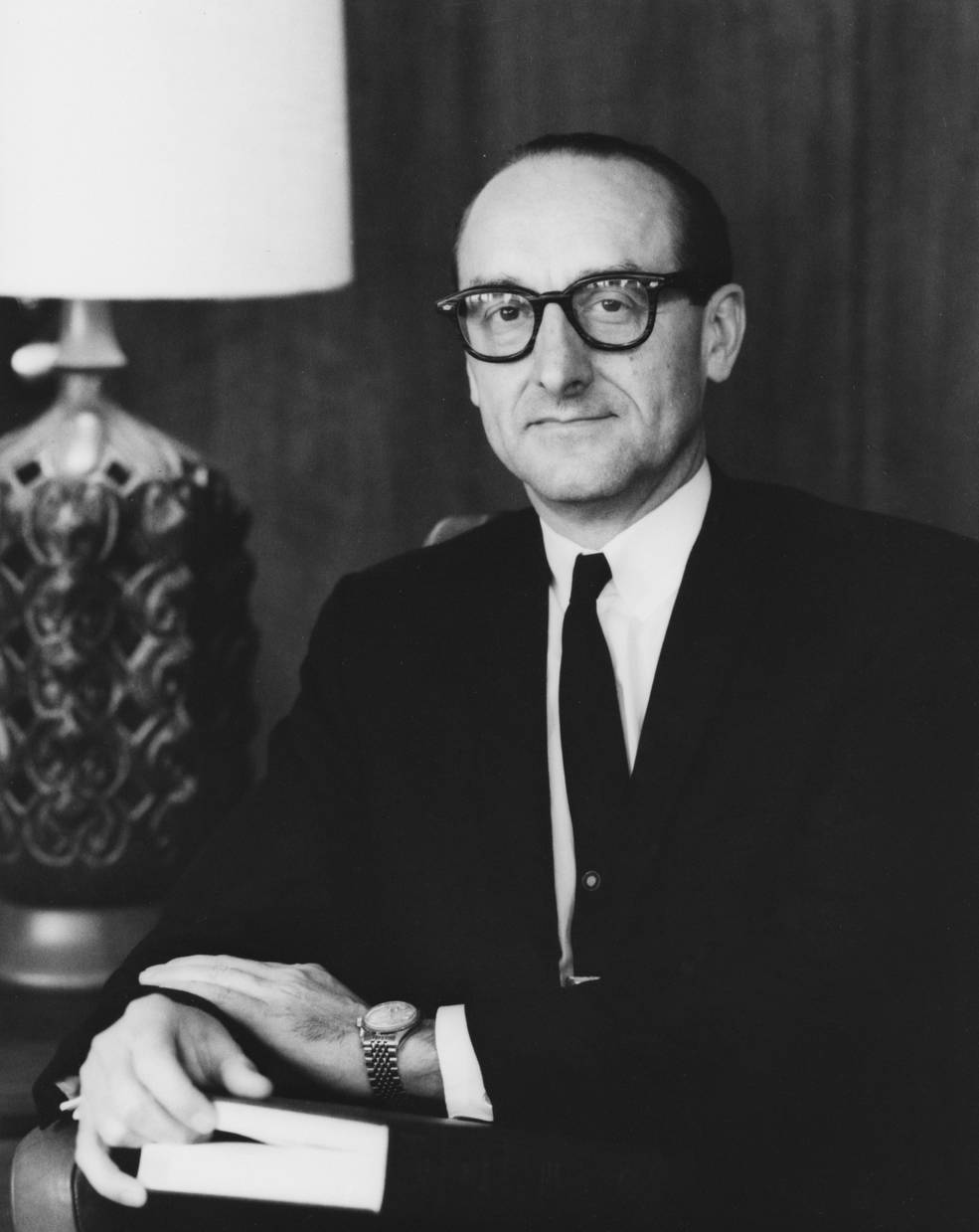
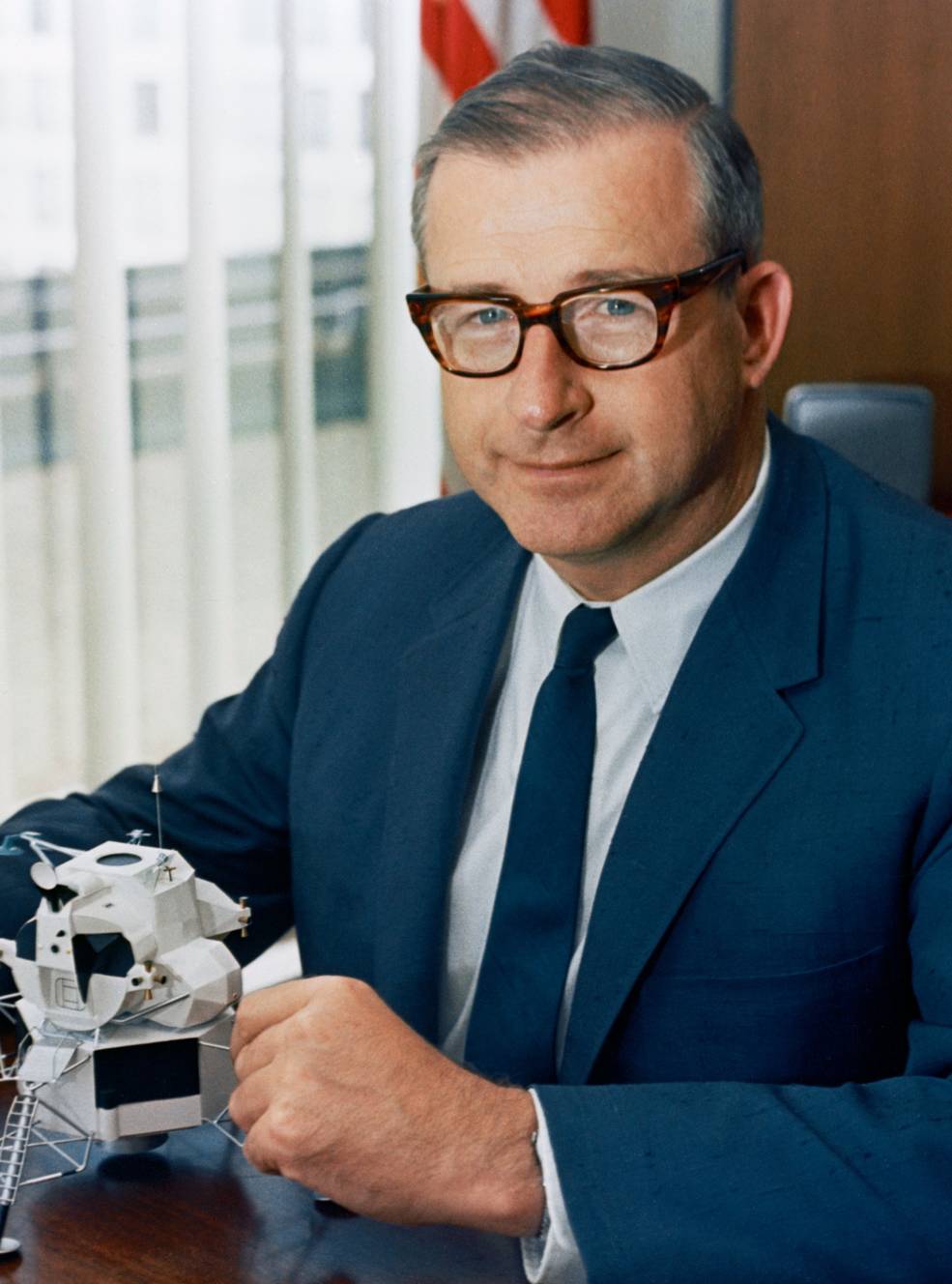
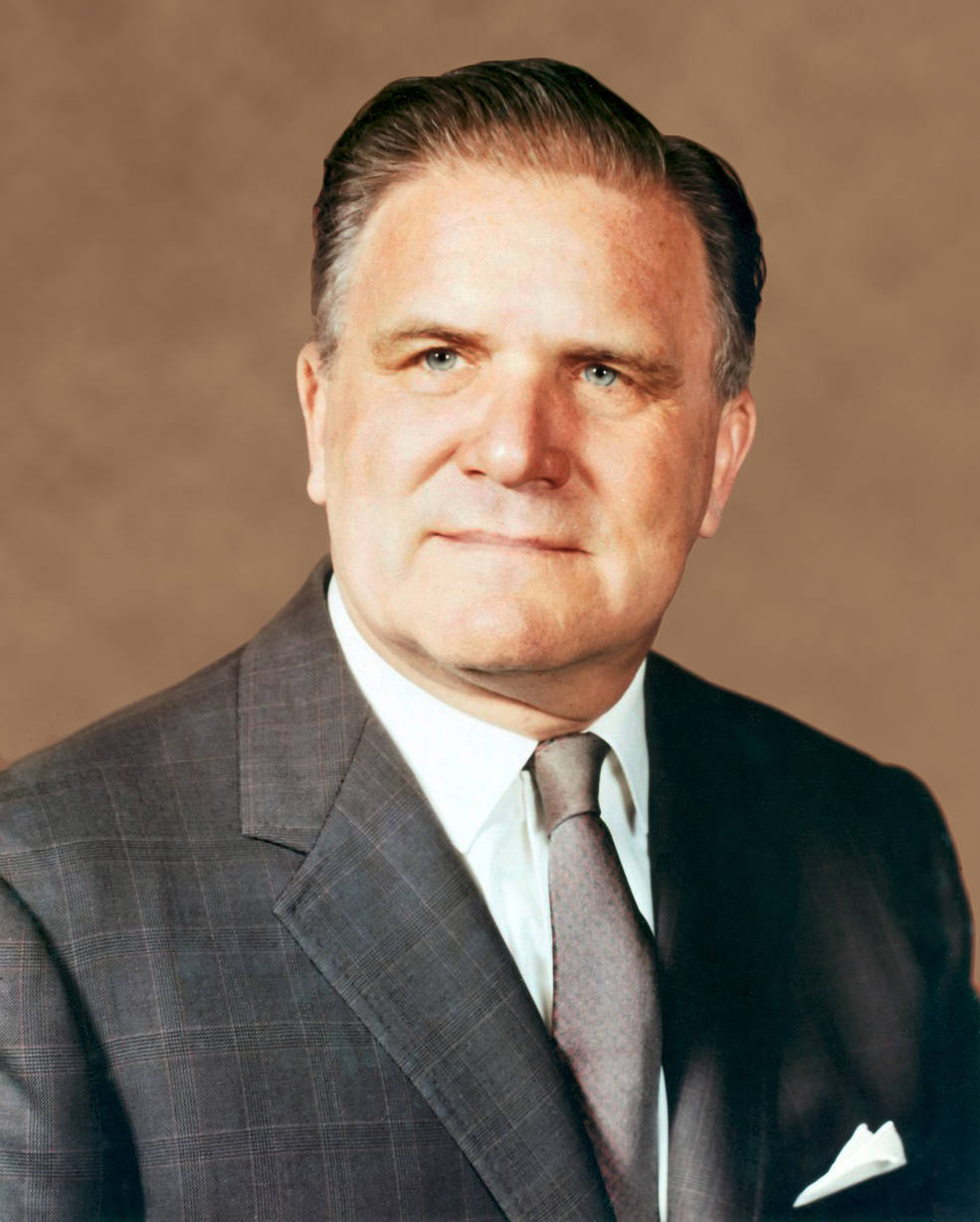


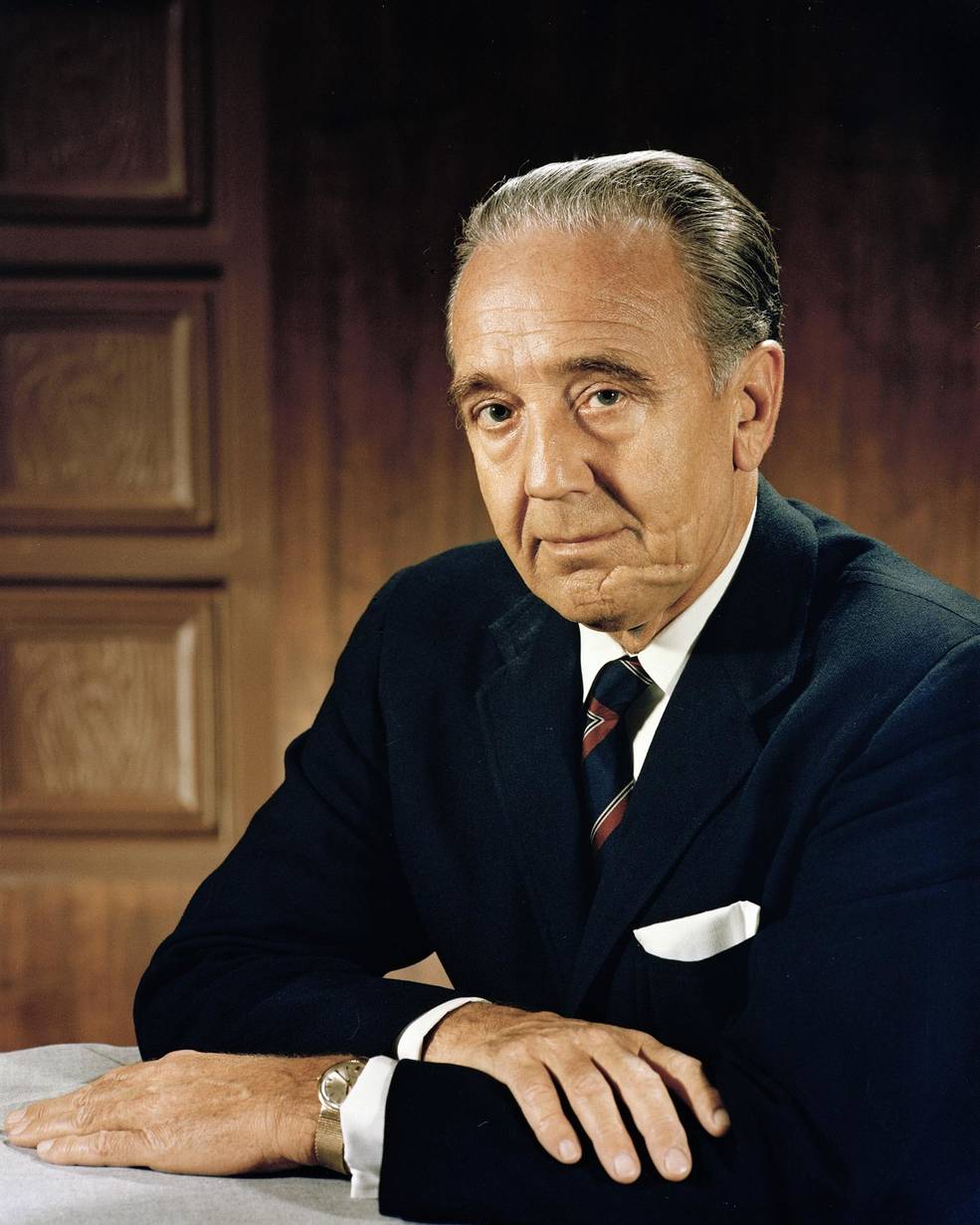
 Left: Apollo Program Director Samuel C. Phillips. Center left: Affiliate Administrator for Manned House Flight George E. Mueller. Center proper: Deputy Administrator Thomas O. Paine. Proper: Administrator James E. Webb.
Left: Apollo Program Director Samuel C. Phillips. Center left: Affiliate Administrator for Manned House Flight George E. Mueller. Center proper: Deputy Administrator Thomas O. Paine. Proper: Administrator James E. Webb.
On Aug. 14, representatives from MSC, MSFC, and KSC attended a meeting in Washington with NASA Deputy Administrator Thomas O. Paine and Apollo Program Director Phillips, the senior Headquarters officers current as NASA Administrator James E. Webb and Affiliate Administrator for Manned House Flight George E. Mueller attended a convention in Vienna. The group mentioned Low’s proposal and agreed on the technical feasibility of engaging in a circumlunar flight with Apollo 8 in December. In the course of the dialogue, Mueller occurred to name from Vienna and after they introduced him with the proposal, he was at first reticent, particularly since NASA had but to fly Apollo 7. He requested extra data and extra time to contemplate the proposal so he may correctly transient Webb. Paine then polled every middle director for his general evaluation. Von Braun, who designed the Saturn V rocket, said that whether or not it went to the Moon or stayed in Earth orbit didn’t matter an excessive amount of. Debus said that KSC may help a Saturn V launch in December – as famous above, his crew was already processing each the rocket and the spacecraft. Gilruth agreed that the proposal represented a key step in reaching President Kennedy’s purpose, and emphasised that the mission shouldn’t simply loop across the Moon however really enter orbit. Following extra discussions after Webb’s return from Vienna, he agreed to the plan, however wouldn’t make a proper determination till after a profitable Apollo 7 flight in October. NASA saved the lunar orbit plan quiet even because the crews started coaching for his or her respective new missions. An announcement on Aug. 19 merely said that Apollo 8 would not carry a LM, because the company continued to evaluate numerous mission goals. In the end, the plan required President Lyndon B. Johnson’s approval.
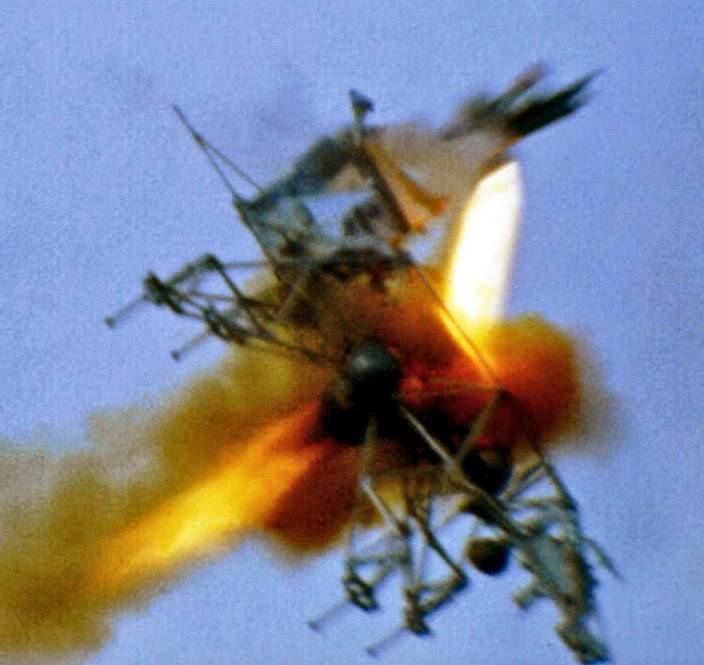
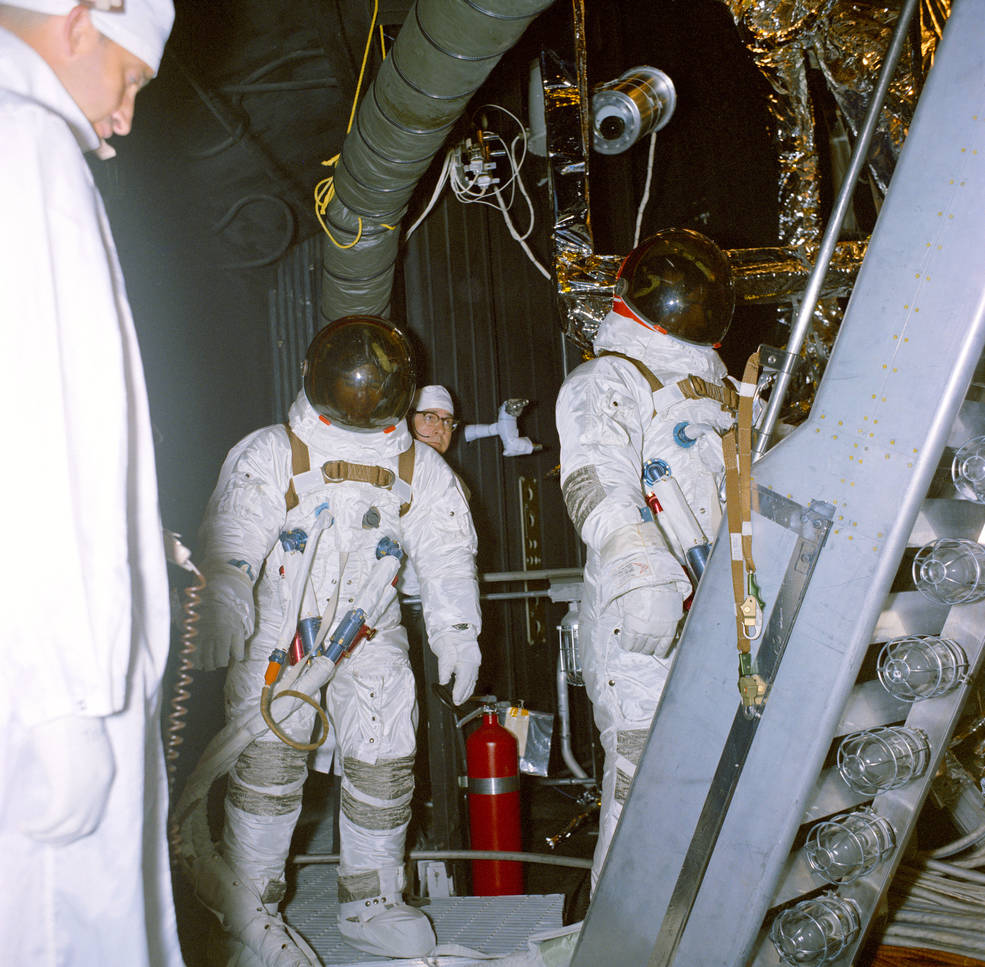
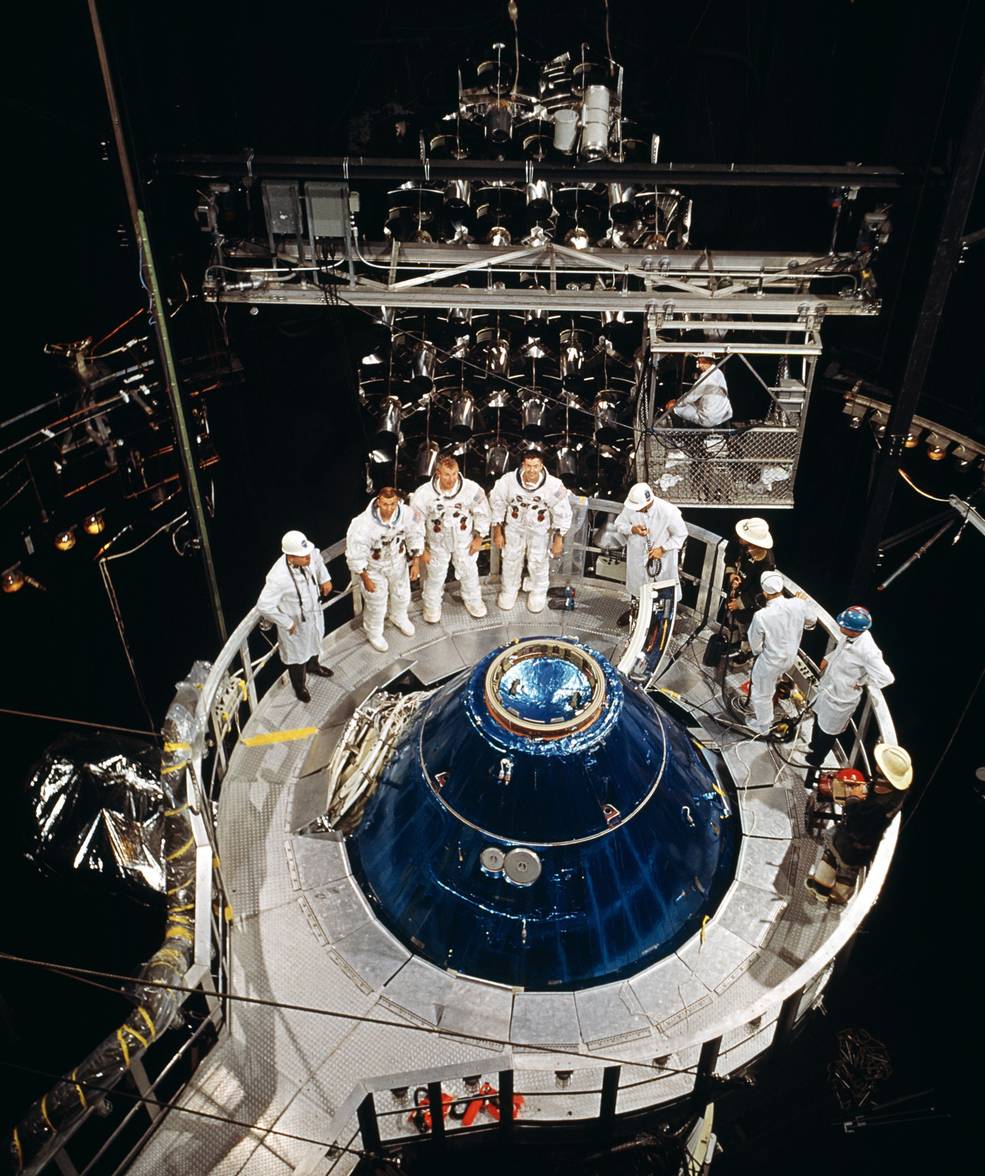
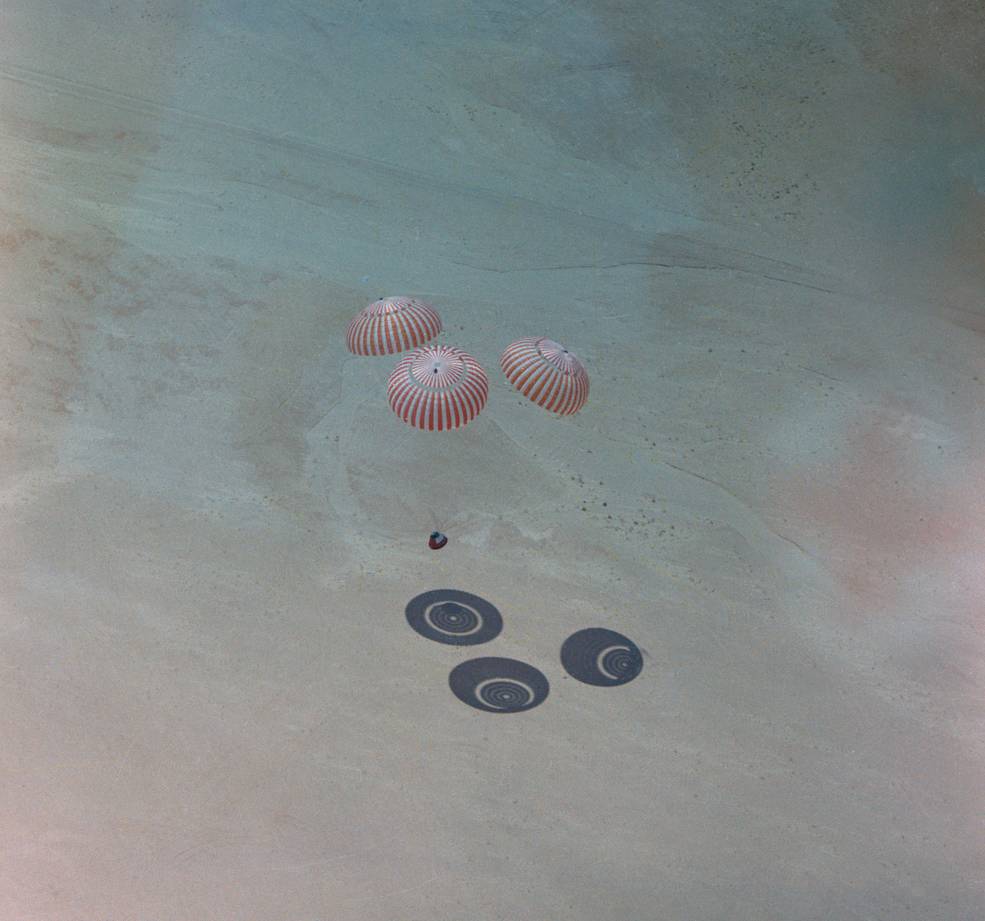


 Left: Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong ejects simply moments earlier than his Lunar Touchdown Analysis Automobile crashed. Center left: Pilot Gerald P. Gibbons, left, and astronaut James B. Irwin put together to enter an altitude chamber for one of many Lunar Module Take a look at Article-8 (LTA-8) vacuum exams. Center proper: Astronauts Joe H. Engle, left, Vance D. Model, and Joseph P. Kerwin getting ready for the 2TV-1 altitude take a look at. Proper: One of many remaining Apollo parachute exams.
Left: Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong ejects simply moments earlier than his Lunar Touchdown Analysis Automobile crashed. Center left: Pilot Gerald P. Gibbons, left, and astronaut James B. Irwin put together to enter an altitude chamber for one of many Lunar Module Take a look at Article-8 (LTA-8) vacuum exams. Center proper: Astronauts Joe H. Engle, left, Vance D. Model, and Joseph P. Kerwin getting ready for the 2TV-1 altitude take a look at. Proper: One of many remaining Apollo parachute exams.
As these discussions happened, work across the nation continued to arrange for the primary lunar touchdown, not with out some setbacks. On Might 8, astronaut Neil A. Armstrongejected simply within the nick of time because the Lunar Touchdown Analysis Automobile (LLRV) he was piloting went uncontrolled and crashed. Managers suspended flights of the LLRV and its successor, the Lunar Touchdown Coaching Automobile (LLTV), till Oct. 3. Astronauts used the LLRV and LLTV to coach for the ultimate few hundred ft of the descent to the Moon’s floor. On Might 27, astronaut James B. Irwin and pilot Gerald P. Gibbons started a sequence of altitude exams in Chamber B of the Space Environment Simulation Laboratory (SESL) at MSC. The exams, utilizing the LM Test Article-8 (LTA-8), evaluated the strain integrity of the LM in addition to the brand new spacesuits designed for the Apollo program. The primary sequence of LTA-8 exams supported the Earth-orbital flight of LM-3 on Apollo 9 whereas a second series in October and November supported the LM-5 flight of Apollo 11, the primary lunar touchdown mission. In June, utilizing SESL’s Chamber A, astronauts Joseph P. Kerwin, Vance D. Brand, and Joe H. Engle accomplished an eight-day thermal vacuum take a look at utilizing the Apollo 2TV-1 spacecraft to certify the car for Apollo 7. A second test in September licensed the car for lunar missions. July 3 marked the ultimate qualification drop take a look at of the Apollo parachute system, a sequence begun 5 years earlier. The exams certified the parachutes for Apollo 7.
Historical past information that Apollo 11 achieved the primary human touchdown on the Moon in July 1969. It’s outstanding to suppose that only one 12 months earlier, with the company nonetheless recovering from the Apollo 1 fireplace, NASA had not but flown any astronauts aboard an Apollo spacecraft. And additional, the company took the daring step to plan for a lunar orbital mission on simply the second crewed mission. With a cadence of a crewed Apollo flight each two months between October 1968 and July 1969, NASA achieved President Kennedy’s purpose of touchdown a person on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth.
John Uri
NASA Johnson House Heart
![[original_title]](https://rawnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/moon_landing_minus_1_year_1_as1-0322-67pc-29143-view_of_fire_damage_to_cm_at_pad_34.jpg)







